NEWS
________________________________________________________________________________________________
Could a Large Distant Earthquake off the Coast of Puerto Rico Cause a Tsunami Along the US East Coast?
Watch Video to Learn More and How NESEC Can Help You to Map Your Risk
Apply Now For Free Tsunami Risk Mapping
_______________________________________________________________________
Social Vulnerability Analysis Using FEMA’s Hazus Software
A Guide For Emergency Managers
WAKEFIELD, MA – In the context of emergency management and disaster planning, Hazus (Hazards US) is a software tool developed by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) to assess the potential impacts of natural disasters on communities. It helps estimate the potential losses and damages to buildings, infrastructure, and populations caused by hazards like tsunami, earthquakes, hurricanes and floods.
Social vulnerability, within the Hazus framework, refers to the susceptibility of certain populations or communities to suffer disproportionate adverse effects during a disaster event. These vulnerabilities are often associated with various socio-economic factors, demographics and access to resources that may impact a community’s ability to prepare for, cope with and recover from a disaster.
While Hazus is a very effective loss estimation tool, its focus and results are primarily for physical and economic damage. While Hazus does include summary reports for shelter needs and casualties, summary reports on other social vulnerability indicators that are vitally important considerations in the event of a damaging disaster, are not currently available. Factors contributing to social vulnerability in in a disaster can include socioeconomic status, age, race, access to transportation, housing conditions, education, etc.
Understanding social vulnerability is crucial for emergency managers, as it helps identify at-risk communities that may require additional support and resources before, during, and after a disaster. By incorporating social vulnerability data into Hazus assessments, emergency planners can better prioritize their response efforts and develop strategies to mitigate the impact on potentially vulnerable populations.
To help identify potentially vulnerable populations, the Northeast States Emergency Consortium (NESEC) has developed a Guide that outlines steps emergency managers and other public safety officials can take to identify potentially vulnerable populations and make decisions to help plan for their safety. This Guide presumes that the user has prior experience using both Hazus and ArcGIS software. For those who do not, Hazus software, training and technical assistance (help) is available from FEMA.
While this Guide focuses on the tsunami hazard, it is applicable to other hazards.
_______________________________________________________________________
Should Governments Plan for a US East Coast Tsunami?
WAKEFIELD, MA – Yes, in the context of all-hazards planning, governments should plan for a potential US East Coast tsunami despite it being a low-probability event. It is essential for governments at various levels (federal, state, county and local) to include tsunamis in their disaster preparedness, response and hazard mitigation plans.
NESEC can help for FREE and here’s why planning is important:
- Hazard Mitigation: Planning allows governments to identify areas at higher risk of tsunamis, assess vulnerabilities, and implement mitigation measures to reduce potential impacts.
- Emergency Preparedness and Response: Developing comprehensive preparedness and response plans ensures that government agencies, emergency services, and relevant stakeholders are prepared to act swiftly and effectively during a tsunami event.
- Public Safety and Education: Governments play a crucial role in raising public awareness about tsunamis and educating communities on preparedness measures. They can disseminate information through various channels including social media platforms to ensure that residents understand the risks and know how to respond in the event of a tsunami.
- Early Warning Systems: Governments can continue to invest in and maintain robust early warning systems that provide timely alerts to coastal communities.
- Research and Monitoring: Governments can continue to support scientific research and monitoring efforts related to tsunamis along the US East Coast. This includes funding studies on potential sources, mapping potential tsunami inundation areas, investing in monitoring equipment and technologies, and collaborating with research institutions to enhance our understanding of regional tsunami hazards.
While the pro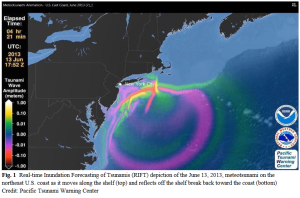 bability of a tsunami along the US East Coast is relatively low, the impact could be significant due to the density of coastal population, property and infrastructure. In addition, the US East Coast is vulnerable to meteotunamis, also known as meteorological tsunamis. This is a type of tsunami that is generated by atmospheric disturbances, such as changes in atmospheric pressure, severe thunderstorms, squalls, or other weather related events. It is important for coastal communities to be aware of the potential risks posed by meteotunamis and to have appropriate monitoring and warning systems in place.
bability of a tsunami along the US East Coast is relatively low, the impact could be significant due to the density of coastal population, property and infrastructure. In addition, the US East Coast is vulnerable to meteotunamis, also known as meteorological tsunamis. This is a type of tsunami that is generated by atmospheric disturbances, such as changes in atmospheric pressure, severe thunderstorms, squalls, or other weather related events. It is important for coastal communities to be aware of the potential risks posed by meteotunamis and to have appropriate monitoring and warning systems in place.
Comprehensive planning allows governments to be proactive, mitigate risks, and protect lives, property and infrastructure. It ensures that the necessary infrastructure, systems, and preparedness measures are in place to respond effectively in the event of a tsunami or other tsunamigenic events.
Tsunami Awareness



Connect
Connect with us on the following social media platforms.